Petrous Carotid Aneurysm Causing Pulsatile Tinnitus: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Article information
Abstract
We present the case of a patient who developed pulsatile tinnitus that was found to be associated with a petrous carotid aneurysm. The aneurysm was successfully obliterated using stent-assisted coiling, after which the patient was symptom-free. Although aneurysms arising from the petrous segment of the internal carotid artery are rare, this pathology must be considered as a causative factor in patients with pulsatile tinnitus. Endovascular treatment appears to have been successful in resolving the symptoms associated with this pathology.
INTRODUCTION
Pulsatile tinnitus is an annoying symptom. Patients presenting with this symptom frequently suffer from insomnia as well; this significantly deteriorates their quality of life.9)10)15) Thus, an accurate diagnosis of the etiology and identification of the proper treatment are important. Jugular bulb diverticula, sigmoid sinus stenosis, dural arteriovenous fistula (AVF), or arteriovenous malformations (AVM) draining into the transverse and sigmoid sinuses have all been reported as common causes of pulsatile tinnitus.5)18)19)21)22)23)24)25) However, a petrous carotid aneurysm causing pulsatile tinnitus is extremely rare.5) Therefore, given the limited number of reported cases and an lack of long-term outcomes, the ideal treatment for this rare lesion has not yet been well. We describe an interesting case of pulsatile tinnitus related to a petrous carotid aneurysm that was treated successfully using stent-assisted coiling. We also discuss the treatment methods employed in the cases previously reported in literature.
CASE REPORT
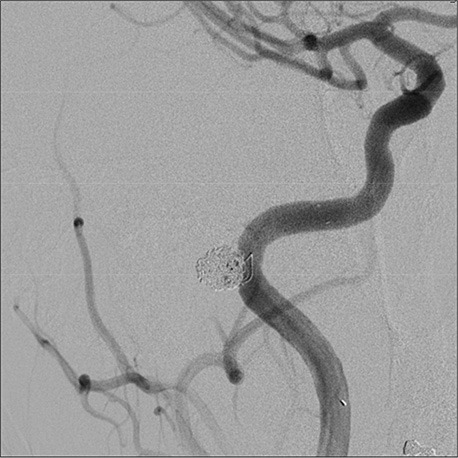
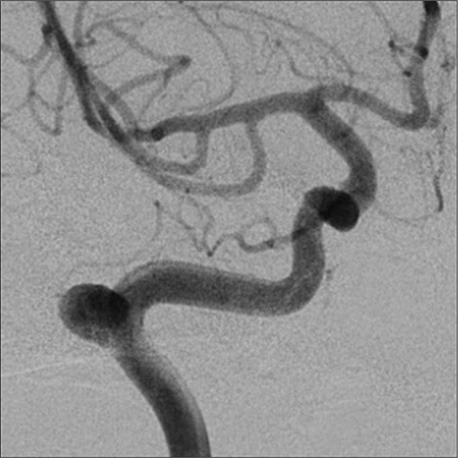
A 41-year-old woman was hospitalized when she visited the Otorhinolaryngology department complaining of a headache and a drumming sound in her right ear. Otolaryngologic examination did not reveal any pathological findings. The patient was referred to our department after brain imaging including magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) revealed a petrous carotid aneurysm (Fig. 1). A digital subtraction angiogram (DSA) was performed for further evaluation; it confirmed an 8-mm- saccular aneurysm with a 6-mm-wide neck (Fig. 2). The patient was prescribed aspirin (200 mg/day) and clopidogrel (75 mg/day) for 7 days as premedication. Femoral artery puncture was performed and 5,000 units of intravenous heparin sodium were administered. A microcatheter was placed within the aneurysm using the jailing technique. To ensure that the coils stay in the aneurysm, a stent was deployed in the right petrous internal carotid artery (ICA) in front of the aneurysm neck. Next, coil embolization was performed using the jailed microcatheter. The final DSA revealed a slight remnant of the neck and almost complete obliteration of the aneurysm with right ICA patency (Fig. 3). After the procedure, both the tinnitus and the headache completely subsided without any neurological deficits. The symptoms heave not recurred during a follow-up period of 4 years.
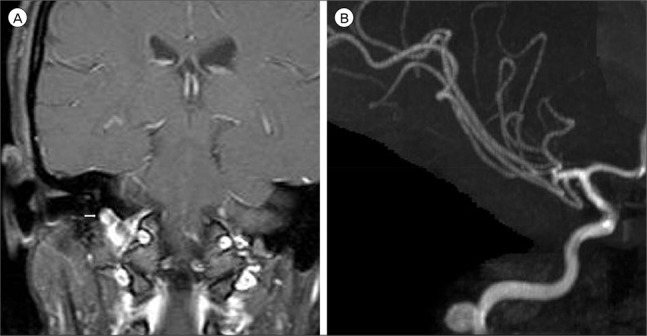
(A) Vascular enlargement bulging into the middle ear (white arrow). (B) MRA revealed an approximately 0.8-cm-sized petrous carotid aneurysm of the right ICA. MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; MRA = magnetic resonance angiography; ICA = internal carotid artery.
DSA confirmed a petrous carotid aneurysm of the right ICA. DSA = digital subtraction angiogram; ICA = internal carotid artery.
DISCUSSION
Around 10% of adults suffer from tinnitus. It often causes insomnia and depression, affecting the quality of life of the affected individuals.10)15) Tinnitus can be classified into pulsatile and non-pulsatile forms, with the former accounting for 10% of all the tinnitus cases.5)15)24)
Pulsatile tinnitus mostly stems from vascular lesions; its pathophysiological mechanism can be described as follows: 1) vessel stenosis or increased blood flow near the inner ear brings about turbulent blood flow, which causes the noise. 2) Bony conductive changes in the inner ear cause the sound of the normal blood flow to be perceived as louder.5)15)25) Pulsatile tinnitus could originate from arteries, veins, AVFs, or tumors.5)15)18)21)23)25) Causes of arterial origin include ICA stenosis, fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD), dissecting ICA, persistent stapedial artery, arterial compressive cochlear nerve, dural AVF, carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF), AVM, cerebral aneurysm, and increased cardiac output have been reported as causes of arterial origin.5)18) These predominantly induce arterial turbulence, which directly exerts a force on the nerves and structures of the adjacent inner ear, resulting in pulsatile tinnitus. Causes of venous origin include high jugular bulb, jugular bulb diverticulum, intracranial hypertension, sigmoid sinus anomaly, and emissary veins.5)7)15)21)22)23) Transverse sinus stenosis has also been reported to cause pulsatile tinnitus.23)25)
According to Hofmann et al.5), the leading cause of pulsatile tinnitus is ICA stenosis, which accounts for 18% of cases. The second most frequent cause is intracranial hypertension (16%), followed by high jugular bulb (12%). Dural arteriovenous fistula is fourth (7%), followed by vascular flow-rich tumors (6%). Tinnitus caused by an aneurysm is rare and accounted for only 1% of the cases. In the case of aneurysm, tinnitus is caused by the turbulent flow that directly exerts force on the cochlear nerve and structures in the inner ear.13)15)19)
The petrous ICA is anatomically related with various structures such as the tensor tympani muscle, Eustachian tube, cochlea, etc.11)13) Thus, lesions in this region can cause pulsatile tinnitus and/or hearing loss.13)19) In our case, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed vascular bulging from the petrous internal carotid (petrous aneurysm) into the Eustachian tube, which is thought to induce pulsatile tinnitus due to either the turbulent flow in the aneurysmal sac or the hammer effect of the aneurysm (Fig. 1A).
Although some studies have reported that a petrous carotid aneurysm may result from trauma, infection, radiation, or a congenital anomaly, the exact cause is unclear.13) In our case, the cause of the petrous carotid aneurysm was unclear.
If no abnormality is seen on an otorhinolaryngology examination in a case of pulsatile tinnitus, there are several probable diagnoses that need to be ruled out. CT angiography (CTA), MRI, or MRA can be used to diagnose pulsatile tinnitus to differentiate intracranial vascular diseases.
A petrous carotid aneurysm causing pulsatile tinnitus is extremely rare.5) Therefore, the right treatment for this rare lesion has not yet been well established due to the limited number of cases and a lack of long-term outcomes.
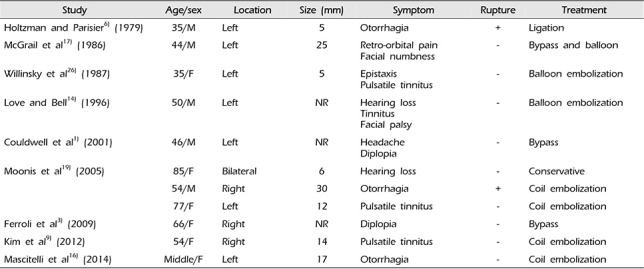
Based on previous reports, the most common treatment methods for the petrous carotid aneurysm are summarized in Table 1: conservative management, endovascular balloon occlusion, aneurysm trapping, and revascularization with bypass, and endovascular coil embolization with or without stent placement.1)2)3)6)9)14)16)17)19)26) Recently, a method using a flow diverter was reported.4) While surgical approaches such as trapping with bypass surgery are effective in relieving the symptoms, they are more difficult to perform, risky, and require a long recovery period.1)3)13)17)20) Recent advances in endovascular technology and devices have resulted in endovascular treatments showing results similar to those of surgical treatment.9)11)13)16)19) Particularly, the efficacy of endosaccular coil embolization while preserving the parent artery was comparable to that of endovascular balloon occlusion with scarification of the parent artery.8)12)19)
In our case, pulsatile tinnitus was thought to be remitted by decreasing the hammer effect and eliminating turbulent flow in the sac through stent assisted-endosaccular coiling. Therefore, after considering the difficulty of the surgical approaches, the lower invasiveness of endovascular approaches and the similar efficacies of surgical and endovascular approaches in relieving the symptoms, endovascular coil treatment with/without stent placement may be preferred in the treatment of petrous carotid aneurysms causing pulsatile tinnitus.9)13)16)
CONCLUSION
Although a petrous carotid aneurysm is extremely rare, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus. Endovascular treatment while preserving the parent artery can be the least invasive and the most optimal course of treatment in relieving the symptoms.
Notes
Disclosure: The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.